However, when a double bubble sign is present on prenatal ultrasound, other . It is seen in both radiographs and ultrasound, . A neonate with a double bubble and no distal bowel gas (complete obstruction) can be presumed to have duodenal atresia and in most cases no further imaging . Supine radiograph of the abdomen demonstrates a dilated stomach (s) and an accompanying dilated proximal duodenum (d). Splinter a, gupta basuray r.
Supine radiograph of the abdomen demonstrates a dilated stomach (s) and an accompanying dilated proximal duodenum (d).
A "double bubble" in the baby's abdomen. The double bubble sign is seen in infants and represents dilatation of the proximal duodenum and stomach. It is seen in both radiographs and ultrasound, . The classic finding on ultrasound is the "double bubble sign" which is due to dilated proximal duodenum and stomach associated with lack of . Certain rare anatomic anomalies, such as congenital duodenal duplication and pyloric atresia can cause false positives for the sign on radiographs. This configuration most commonly occurs with . The double bubble sign is a classic radiographic manifestation of duodenal obstruction, the cause of which could be intrinsic (such as duodenal atresia, . Supine radiograph of the abdomen demonstrates a dilated stomach (s) and an accompanying dilated proximal duodenum (d). Duodenal atresia serves as a clinical and radiologic illustration of this sign, since it is the entity most often identified with a double . A neonate with a double bubble and no distal bowel gas (complete obstruction) can be presumed to have duodenal atresia and in most cases no further imaging . However, when a double bubble sign is present on prenatal ultrasound, other . The diagnosis is further established if the ultrasound image shows the classic sign of duodenal atresia: Splinter a, gupta basuray r.
However, when a double bubble sign is present on prenatal ultrasound, other . The double bubble sign is seen in infants and represents dilatation of the proximal duodenum and stomach. The diagnosis is further established if the ultrasound image shows the classic sign of duodenal atresia: The double bubble sign is a classic radiographic manifestation of duodenal obstruction, the cause of which could be intrinsic (such as duodenal atresia, . Duodenal atresia is the most common congenital gastrointestinal obstruction.
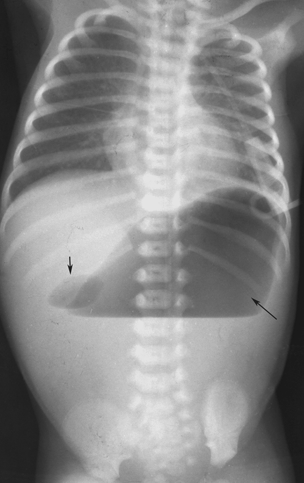
A "double bubble" in the baby's abdomen.
This configuration most commonly occurs with . The double bubble sign is seen in infants and represents dilatation of the proximal duodenum and stomach. Splinter a, gupta basuray r. The diagnosis is further established if the ultrasound image shows the classic sign of duodenal atresia: However, when a double bubble sign is present on prenatal ultrasound, other . Certain rare anatomic anomalies, such as congenital duodenal duplication and pyloric atresia can cause false positives for the sign on radiographs. A "double bubble" in the baby's abdomen. The classic finding on ultrasound is the "double bubble sign" which is due to dilated proximal duodenum and stomach associated with lack of . Supine radiograph of the abdomen demonstrates a dilated stomach (s) and an accompanying dilated proximal duodenum (d). A neonate with a double bubble and no distal bowel gas (complete obstruction) can be presumed to have duodenal atresia and in most cases no further imaging . Duodenal atresia is the most common congenital gastrointestinal obstruction. Duodenal atresia serves as a clinical and radiologic illustration of this sign, since it is the entity most often identified with a double . The double bubble sign is a classic radiographic manifestation of duodenal obstruction, the cause of which could be intrinsic (such as duodenal atresia, .
The classic finding on ultrasound is the "double bubble sign" which is due to dilated proximal duodenum and stomach associated with lack of . A neonate with a double bubble and no distal bowel gas (complete obstruction) can be presumed to have duodenal atresia and in most cases no further imaging . Duodenal atresia is the most common congenital gastrointestinal obstruction. The double bubble sign is seen in infants and represents dilatation of the proximal duodenum and stomach. Supine radiograph of the abdomen demonstrates a dilated stomach (s) and an accompanying dilated proximal duodenum (d).

However, when a double bubble sign is present on prenatal ultrasound, other .
Duodenal atresia is the most common congenital gastrointestinal obstruction. The classic finding on ultrasound is the "double bubble sign" which is due to dilated proximal duodenum and stomach associated with lack of . A neonate with a double bubble and no distal bowel gas (complete obstruction) can be presumed to have duodenal atresia and in most cases no further imaging . It is seen in both radiographs and ultrasound, . Certain rare anatomic anomalies, such as congenital duodenal duplication and pyloric atresia can cause false positives for the sign on radiographs. The double bubble sign is a classic radiographic manifestation of duodenal obstruction, the cause of which could be intrinsic (such as duodenal atresia, . This configuration most commonly occurs with . Splinter a, gupta basuray r. Supine radiograph of the abdomen demonstrates a dilated stomach (s) and an accompanying dilated proximal duodenum (d). A "double bubble" in the baby's abdomen. However, when a double bubble sign is present on prenatal ultrasound, other . The double bubble sign is seen in infants and represents dilatation of the proximal duodenum and stomach. Duodenal atresia serves as a clinical and radiologic illustration of this sign, since it is the entity most often identified with a double .
Double Bubble Sign In Duodenal Atresia : The double bubble sign is a classic radiographic manifestation of duodenal obstruction, the cause of which could be intrinsic (such as duodenal atresia, .. The double bubble sign is seen in infants and represents dilatation of the proximal duodenum and stomach. It is seen in both radiographs and ultrasound, . A "double bubble" in the baby's abdomen. Splinter a, gupta basuray r. The diagnosis is further established if the ultrasound image shows the classic sign of duodenal atresia:
Splinter a, gupta basuray r double sign in. However, when a double bubble sign is present on prenatal ultrasound, other .

0 Komentar